Developers must now show how they will improve the biodiversity of their development site as a result of their works. Developers must record the (baseline) on-site habitats that exist before development starts and show how they will either enhance or replace these on site. If their proposals fail to reach the 10% threshold, the developer may provide the shortfall elsewhere. This post-development mitigation should be done as closely as possible to the development site, or at least within the Local Authority. However, if this isn’t possible, they can use approved sites anywhere in England.
This approach is called the Biodiversity Gain Hierarchy (found in Schedule 7A of the Town and Country Planning Act 1990 at section 37A). The Hierarchy says it’s a priority to avoid the ‘adverse effects’ to ‘onsite habitat with a habitat distinctiveness score … equal to or higher than four.’ If this can’t be avoided, only then is mitigation permitted. In our experience, nearly all developers ignore the requirement to avoid adverse effects and move straight on to mitigation.
Since the introduction of the Bristol Tree Replacement Standard in 2013, developers (and planners) have ignored the policy requirement to avoid tree removal where at all possible. Instead, they’ve moved straight on to providing compensation for the trees lost to the development. As a result, the money set aside for replacement tree planting was not spent (on occasion reaching nearly £1 million) and many of the lost trees were never replaced.
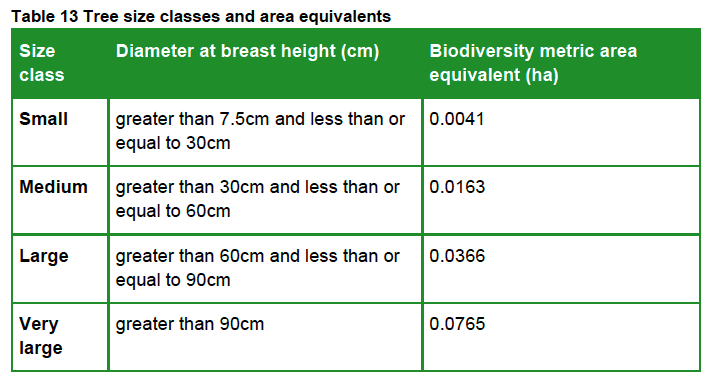
Under the Hierarchy, habitats that score four are designated as having medium distinctiveness. While many habitats have medium distinctiveness, many don’t. For example, managed grassed areas (called ‘modified grassland’) are often found on urban sites but have a low distinctiveness score. So, too, do many other urban habitats such as allotments and gardens. Developers are not required to avoid harming these, though losses to these habitats must still be mitigated.
There’s no definition of what an ‘adverse effect’ is or any guidance on how it is assessed. However, recent advice from the Bristol’s Chief Planner about the meaning of ‘harm’ suggests that this could be interpreted very broadly or simply ignored because some sort of mitigation will always be available.
In the last extreme, developers may purchase biodiversity credits. We wait to see how this and the offsite biodiversity mitigation market evolves, but a 2012 paper published in the Harvard Environmental Law Review suggests that such environmental markets are prisoners of their own geography because the space available is always constrained:
Markets for water quality, biodiversity, endangered species, fisheries, air quality, and aquatic resources, to name a few, must recognize that the commodities they trade exist at particular geographic scales, and set appropriate spatial limits on the redistribution of environmental quality. The size of geographic trading areas has significant implications for the economic viability of markets and the ecological quality of their offsets.
This will be a particular challenge when providing biodiversity mitigation in urban areas.
The squeeze on green spaces
Land use in Bristol is subject to intense competition by many stakeholders. This is especially true for our green and open spaces, which offer many ‘services’ beyond just habitat provision. There is very little, if any, space available for new biodiversity to be created. At best, some green spaces might be enhanced, but opportunities to do this are likely to be very limited.
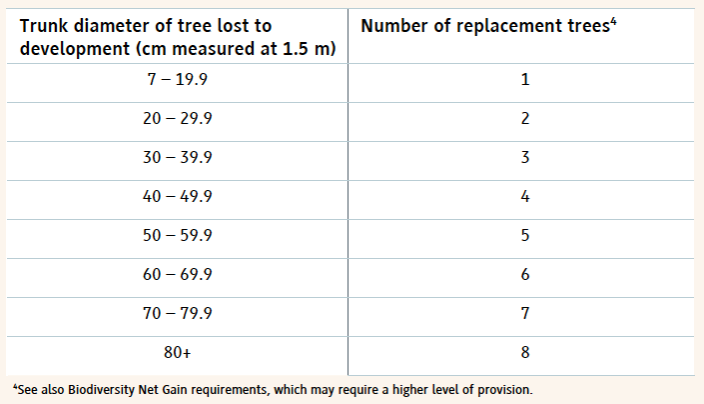
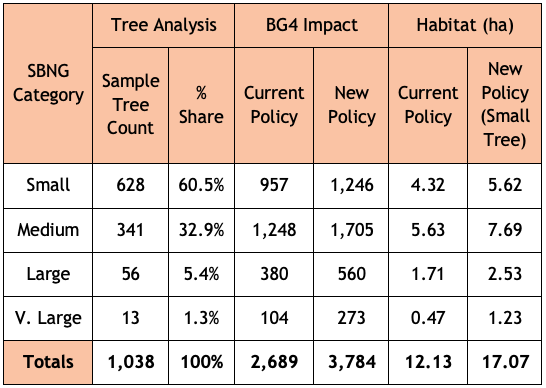
For example, Bristol Tree Forum’s examination of the three proposals to develop Bedminster Green shows that, if these proposals are allowed, then nearly 400 new trees will need to be planted to compensate for the lost tree habitat – a medium distinctiveness habitat. There’s no room to plant these trees on site, so offsite provision will be needed. There are very few opportunities for doing any new tree planting (as opposed to replacing lost trees) in the surrounding wards or even across Bristol, let alone, as is usually required, within a mile of a development site.

Instead, these replacement trees will have to be planted somewhere else: ‘in some foreign field that is forever Bristol’. This will inevitably lead to a net loss of biodiversity across the city as nature is ‘hollowed out’. This is unacceptable. The whole purpose of the new biodiversity gain regime is to improve overall local biodiversity, but it seems inevitable that Bristol will instead see a steady, inexorable decline.
We are disappointed that the current draft of the new Local Plan addresses none of these issues and have said so in our responses to the latest consultation:
Bristol Tree Forum representations in relation to the Bristol Local Plan 2023 Publication Version consultation & BTF Representations on the Bristol Local Plan 2023 publication version – Addendum.

A shorter version of this article was published by 24/7 as:
‘It seems inevitable Bristol will see a steady, inexorable biodiversity decline’