We even wrote an open letter to the Chief Planner asking them to explain their reasoning. We published this as a blog: It seems that SNCIs are nothing special – an open letter to Bristol’s Chief planner.
Update
Unbeknown to us, it seems that the Council’s Nature Conservation officer did comment on the Chief Planner’s earlier advice to the Committee:

This document was disclosed on 1 December 2023 as a result of our Freedom of Information request of 01 November 2023. This appears to have formed the basis of the answers given below.
Update Ends
As we received no reply at the time, we took the opportunity to ask again when the Committee reconvened to make its decision on 29 November 2023. We asked two questions – see page 9 of the Public Forum. As the responses still didn’t really satisfy, we asked two supplementary questions:
- When you say, ‘the site’, what do you mean? Is it within the redline boundary or something else such as within the SNCI’s boundary?
- You say ‘The crucial additional clarification to highlight, is that to be in alignment with this policy it is NOT the overall biodiversity gain that is determinative. There rather needs to be an assessment that establishes whether there is harm with reference to the specific characteristics that make the site special.’
Does this mean that the replacement of one habitat which forms part of the ‘specific characteristics that make the site special’ – such as a replacing the Grassland Habitat that forms part of the current SNCI designation with a Lake Habitat that does not form part of the current SNCI designation, or that the provision of offsite mitigation measures to compensate for onsite habitat losses (in this case -6.44%) – would not be acceptable?
These were the replies:
To question 1
By ‘the site’, it’s the site as set out in the application document, so it’s the SNCI as contained in the application document the area in the redline boundary.
To question 2 (as it is quite complex, we have reproduced it verbatim)
You need to take the application as a whole and where it is demonstrated as that with regard to the features, particularly the grassland, that there is no impact ultimately or, if anything, a slight enhanced impact.
We intervened to ask – So you are saying that the substitution of the grassland habitat for a lake habitat…?
I am not saying that at all, I am saying that the grassland, actually that there is more grassland and that’s what the ecology report also says – more grassland of the type for which the SNCI is designated will be there through this application than before… within the redline boundary.
Here is the recording of this exchange – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-8EvqLA8-Lg (08:05 minutes from the start to 11:30 minutes).
What’s a redline boundary?
Anyone who wants to develop land must produce a location plan of the area proposed for development, delineated by a red line – the so-called ‘redline boundary’.[1]
When planning permission is granted, only the area within the redline boundary may be developed (though ancillary works may take place elsewhere).
Here is the location plan for the South Bristol Cemetery Extension application:
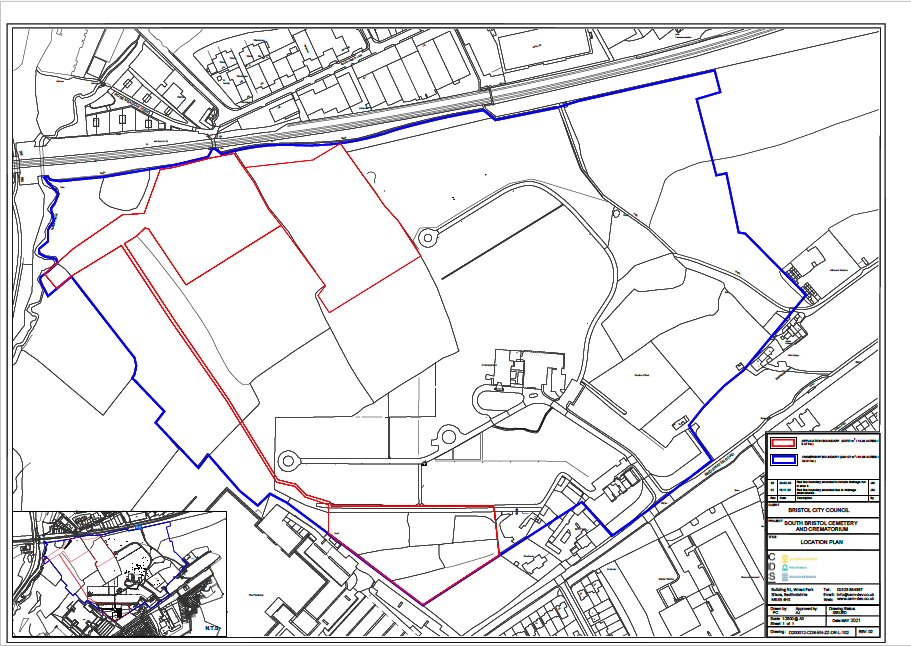
The South Bristol Cemetery Extension location plan (North is at the top)
The redline boundary here is quite complex because it’s made up of two burial areas, in the north and south, and an attenuation pond to collect runoff from the northern burial ground through a series of drains (the southern burial ground runoff will drain straight into Colliter’s Brook to the west). The area within the blue line is also owned by the Council and so is under their control.
The redline boundary is also important when it comes to calculating the biodiversity value (BNG) of the development site. All the habitats within the redline boundary are treated as ‘onsite’, while those outside the boundary are treated as ‘offsite’.
So, when we are told that ‘… there is more grassland and that’s what the ecology report also says – more grassland of the type for which the SNCI is designated will be there through this application than before… within the redline boundary,’ it’s just the onsite area that’s being referred to. This is important, as we show below.
The headline results shown in the most recent BNG 3.1 calculation relied on by the Council[2] show that 6.44% of the baseline onsite area biodiversity will be lost as a result of the development (see Figure 1).
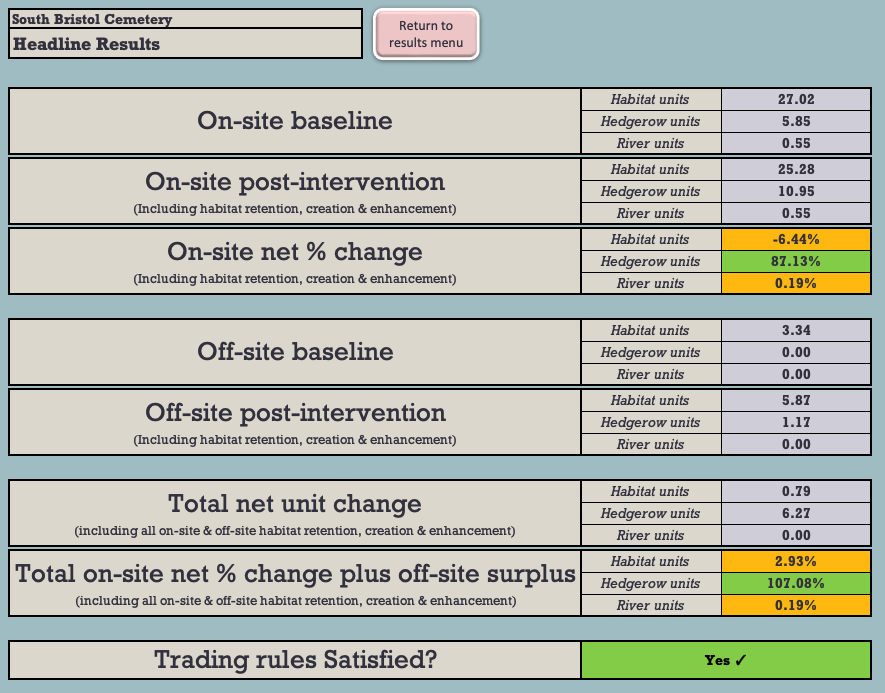
Figure 1: The BNG 3.1 Headline BNG results.
Figure 2 shows the net losses of the onsite grassland habitat:
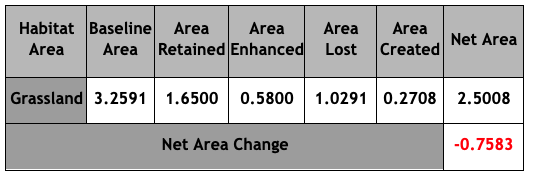
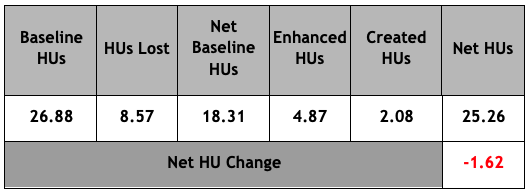
Figure 2: Grassland Area & Habitat Unit analysis (HUs)
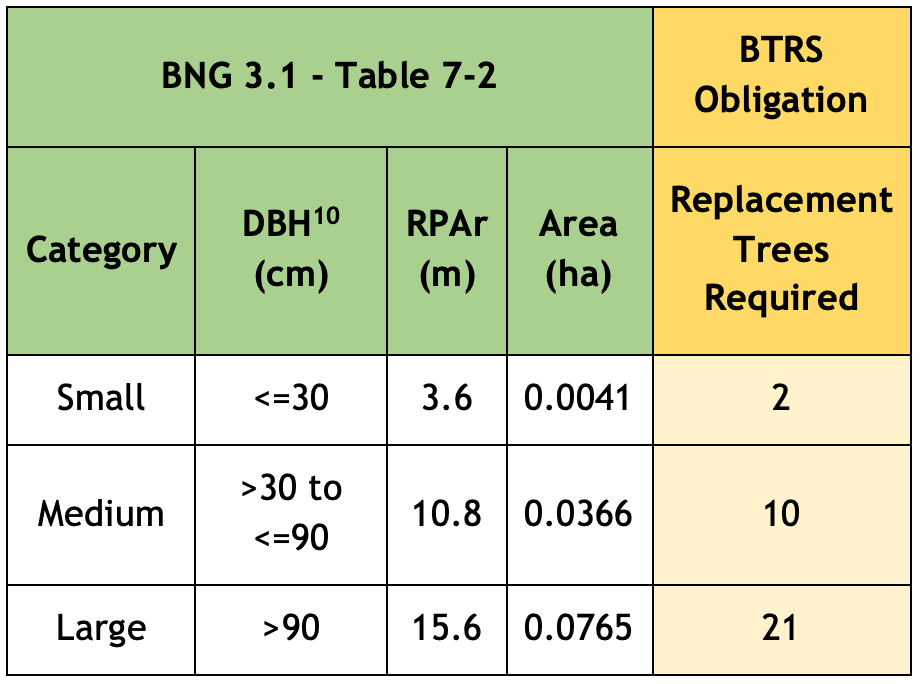
Under the BNG Trading Rules, Medium Distinctiveness grassland habitats may only be replaced with the other Medium Distinctiveness grassland habitats or with habitats of a Higher Distinctiveness. So, in order to achieve the net 2.93% BNG which the Council claims will result from the development, it will be necessary to compensate for these losses by crediting 3.25 Habitat Units of High Distinctiveness Lakes habitat by creating the attenuation pond.
This is not what we are told is happening and it certainly cannot be said that: ‘… there is more grassland … of the type for which the SNCI is designated … within the redline boundary,’ This is plainly untrue and, even on the Chief Planner’s definition (which we do not accept), it is clear that this application will ‘have a harmful impact on the nature conservation value of a Site of Nature Conservation Interest.’ This is contrary to DM19.
What’s more, even if the proposed offsite habitat mitigations were taken into account, there’d still be a net loss of -0.47 HU of Medium Distinctiveness grassland habitat (see Figure 4 below).
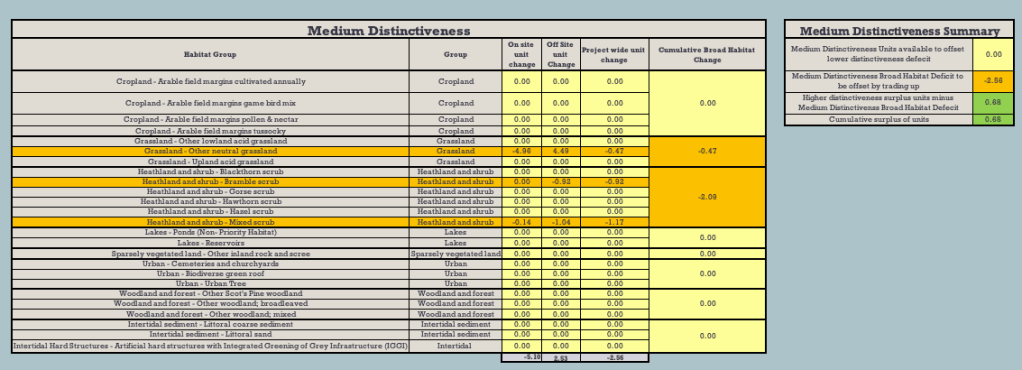
Figure 4: Net Medium Distinctiveness habitat losses
There’s one other serious flaw in the application, which was not brought to the attention of the Development Control Committee at its meeting. There’s a shortfall of -0.11 Habitat Units of the High Distinctiveness habitat, Species-rich native hedgerow with trees. Lost High Distinctiveness habitats may only be replaced like-for-like. This has not happened. As a result, the application is in breach of the BNG Trading Rules and should not have been approved.
We have brought this to the attention of the Council and the LPA.
These are just some of the important reasons why we say that the Development Control Committee was wrong to grant this flawed application.
A copy of this blog can be downloaded here – The saga of the SNCI at Yew Tree Farm continues
[1] It seems that no one thought of those with red/green colour blindness, who might find it difficult to see this red line.
[2] 22_05714_FB-SOUTH_BRISTOL_CEMETERY_BNG__25TH_AUGUST_23_-3540800